- Visibility 77 Views
- Downloads 10 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijmmtd.2024.065
-
CrossMark
- Citation
A retrospective observational study on clinical & radiological profile of patients diagnosed with RT PCR confirmed influenza infection admitted in tertiary care centre
Introduction
Influenza is a serious respiratory illness that can be debilitating and cause complications that lead to hospitalization and death, especially in the elderly. Every year, the global burden of influenza epidemics is believed to be 3-5 million cases of severe illness and 300 000-500 000 deaths. The risk of serious illness and death is highest among persons older than 65 years, children younger than 2 years, and among individuals who have medical conditions that place them at increased risk of developing complications from influenza.[1]
The introduction of these viruses into human populations is responsible for periodic worldwide influenza pandemics. At the level of individual patients both influenza A and B viruses cause clinically indistinguishable disease.
H1N1 is also known as “swine flu” and it is a novel strain of Influenza A virus that evolved by genetic reassortment.[2], [3] It leads to annual epidemics of varying severity. Pandemic of H1N1 first emerged in 2009 April, which was started in Mexico and soon expanded globally.[4], [5] In India, the first case was identified on 2009 May 16, in Hyderabad.[6]
Influenza always had potential to cause widespread pandemics whenever a new type of Influenza strain appeared in the human population and then spread easily from person to person.[2]
Reports indicate that the majority of these cases involved young adults. H1N1 Strain A/California/04/2009—was mainly responsible for this outbreak in India.[3] WHO raised worldwide pandemic alert for swine flu on June 11, 2009, after first case in Mexico which was first of its kind in past 70 years.[7] In India, index cases were reported from Pune (Maharashtra) in May 2009. Since then there is progressive increase in the number of swine flu cases all over the subcontinent. From May 2009 till February 28, 2010, samples from 128,627 persons were tested for 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza across the country and 29,652 (23.05%) of them were found to be positive.[8]
Many patients needed ICU management and close monitoring in swine flu isolation ward. Clinical and radiological findings have been described in such patients in the past. However fewer studies have been published describing clinical and radiological correlation in confirmed patients with H1N1 influenza admitted. Hence we have conducted study that describes the clinical and radiographic findings in confirmed H1N1 influenza patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), along with their correlation with outcome.
Aims and Objectives
To evaluate clinical and radiological profile of the patients admitted with confirmed microbiological cases of Influenza infection.
To examine the risk factors and prognosis of confirmed cases of influenza infection.
Materials and Methods
It is Retrospective Observational study in which a total number of 48 patients diagnosed with confirmed influenza infection by multiplex RT PCR admitted in Department of Respiratory Medicine Metro Hospitals, NOIDA from June 2019 to June 2021 were selected as the study population.
Inclusion Criteria
All patients with confirmed case of Influenza infection.
Exclusion Criteria
Pregnancy
Age < 18 years
The data obtained from hospital files was classified and refined. Relevant history, clinical manifestations , investigations (Radiological), requirement for ventilation, use of other supportive measures and outcome of all the cases were also recorded.
Detection of Influenza A virus was done by Multiplex probe PCR kit(HiGenoMB).
Statistical analysis
Data entered in excel analyzed using the IBM SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) statistical program version 20. The descriptive analysis included generating frequency tables. Graphs (bar graphs, pie chart etc.) generated to depict the data graphically using Excel.
Results
Demographic parameters
Age wise distribution
In our study from the 48 RT PCR confirmed cases , we found that majority of patients (26) 54.17% belonged to 41-60 age group followed by (15) 31.25% patients in 18 -40 age group. Elderly patients i.e. (7) 14.58 % patient were in age group more than 60 years. Mean age was found to be 38.421 ± 10.15
Gender distribution
In present study we found preponderance of males over females. 29 (60.417%) out of 48 patients were males, while 19 (39.583%) were females.
Clinical parameters
Frequency of influenza symptoms
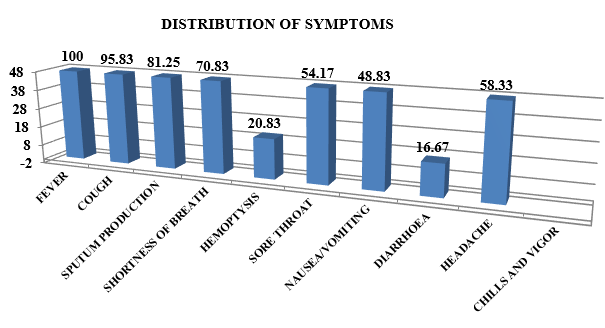
In our study we found that all 48 (100%) patients were presented with fever followed by 46 patients (95.83%) came with complaints of cough and 39 (81.25%) with complaints of sputum production while 34 (70.83%) had complaints of shortness of breath. Hemoptysis 10 (20.83%), sore throat 26 (54.17%), nausea and vomiting (45.83%), diarrhea 8 (16.67%), headache 28 (58.33%) were among other complaints presented in our study.([Figure 1])
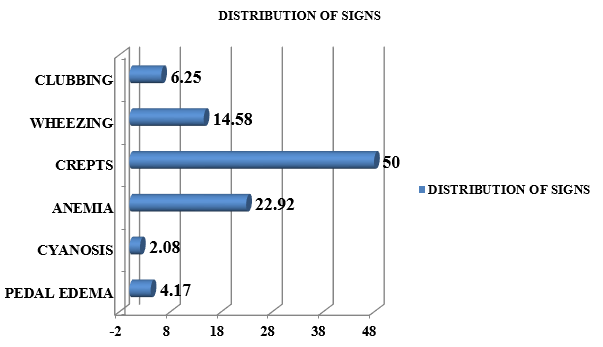
In our study we found that 24 (50%) patients showed crepitation as a major sign of infection. 11 (22.92%) patients were diagnosed with anemia. 7 (14.58%) patients had wheezing while 3 (6.25%) patients had clubbing as sign. Only 1 (2.08%) patient had cyanosis while 2 (4.17%) patients had pedal edema.([Figure 2])
Distribution of co-morbidity
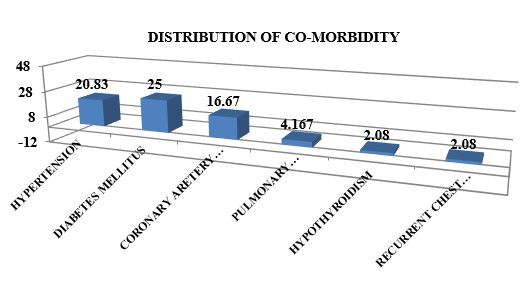
Out of 48 patients 34 (70.83%) patients were observed had other co-morbidities , 12 (25%) had diabetes mellitus and 10 (20.83%) had hypertension. Coronary artery disease was found in 8 (16.67%) patients. Patient had history of old Pulmonary tuberculosis 2 (4.167%), hypothyroidism 1 (2.08%) and recurrent chest infections in childhood 1 (2.08%) amongst other co-morbidities presented.([Figure 3])
Radiological findings
Majority of patients, 27 (56.25%) had bilateral lung involvement while 9 (18.75%) patients had only left lung involvement and 12 (25%) patients had only right lung involvement.
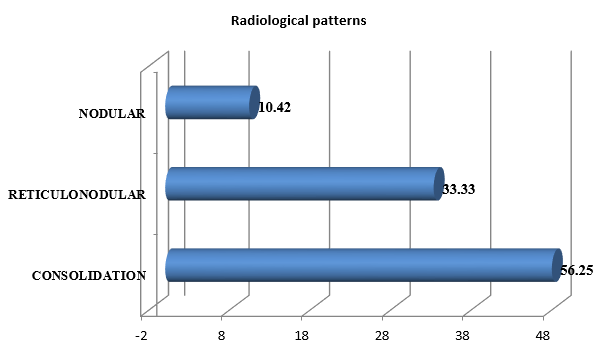
The most common observed radiological pattern was patchy consolidation in 27 (56.25%) patients followed by reticulonodular 16 (33.33%) and nodular 5 (10.42%).([Figure 4])
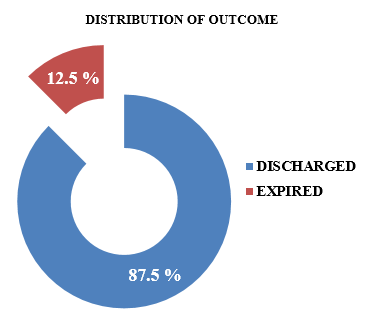
Distribution of outcome
Out of 48 patients in our study, 42 (87.5%) patients were successfully discharged after recovery and 6 (12.5%) patients expired during treatment. Ratio of mortality was found to be 7:1.([Figure 5])
Discussion
In order to determine the relationship between certain relevant prognostic factors and influenza associated hospitalisation and mortality , we performed a cross-sectional retrospective analysis. These variables included the presence of infiltrates on chest radiography, certain comorbidities and need for mechanical ventilation. In our investigation, out of 210 screened H1N1 PCR cases, 48 (22.8%) samples tested positive. In Rajasthan, India, suspected and confirmed cases of pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection were examined using a retrospective descriptive, record-based approach and Similar to the results of the current study, 6203 (34.10%) out of 18,187 examined cases showed positive results. [9] Samara T. et al also found 17.35% positivity in their study. [10]
Baseline characteristics
As we know seasonal influenza typically affects older persons but the 2009 H1N1 influenza had a major negative impact on younger people. In our study, out of 48 cases, most of the cases involved people between the ages of 41 and 60 and the ratio of male to female was 1.52:1. Cheng et al. and Sharma et al. found the lower proportion of patients over 60 in their study may be partially explained by the inclusion of paediatric and juvenile patients. [11], [12] But a higher percentage of women (62%) and 70% patients under 60 years of age was seen in another report by Albarran-Sanchez et al.[13] According to the Report on Surveillance of Influenza in Spain out of 258 patients , 51.1% were men with mean age of 64.5 years. [14] An additional investigation by Monika Maheshwari and Sanjeev Maheshwari in Rajasthan revealed that out of the 94 PCR-confirmed influenza positive cases, 32 (34%) were male and 62 (66%) female, with a median age of 35. [15]
Clinical features
Fever and respiratory failure, which affected over 80% of patients in our study, were the most common clinical characteristics; However, it should be highlighted that patients with pauci-symptoms accounted for around 35% of the total.
These findings confirm prevalence of febrile illness was much higher and fewer cases of respiratory insufficiency similar to studies done by Tabarsi et al., IorioRovina et al., Chawla et al.[16], [17], [18] Upper respiratory symptoms such as cough, and sore throat are typical signs of seasonal influenza as seen in our study. Apart from these symptoms we also found haemoptysis in 10 individuals, and shortness of breath in 34 cases. We link this to the tracheobronchial tree's participation and potential congestion or inflammation there. Other sign and symptoms seen in our series were pedal edema, anemia, asthma, coughing and crepitus. One of the patients had cyanosis. These symptoms are related to how the virus progresses pathologically.
Monika Maheshwari and Sanjeev Maheshwari from Rajasthan did another study which revealed that common presenting symptoms are fever (83.8%), cough (79.4%), dyspnoea (67.1%), rhinorrhea / common cold (25.65%), throat discomfort (13.8%), chest pain (5.3%), and haemoptysis (4.2%) as they examined the clinical and radiological profiles of the patients admitted with confirmed H1N1 infection.[15] In the study of Borse R T et al Cough (96%), Fever (95%), breathlessness (83%), throat pain (34%), crepitations (69%), Tachypnoea (59%)were the prominent symptoms and signs among 100 RT-PCR confirmed patients.[19]
In central India, Arbat S et al. carried out a retrospective investigation to examine the clinical characteristics of swine flu/influenza A H1N1 infection involving 171 cases. As the main complaints, they discovered fever (85%), throat discomfort (51%), and cough (89%), with an average duration of 4.9 days. Cough (100%) was the most common symptom in the study followed by throat discomfort (96.9%), common cold (93.8%), fever (93.8%), and dyspnoea (83.1%).[20] In our investigation, fever (98.7%), cough (61.8%), and increasing dyspnoea (41%), were the most often occurring presenting symptoms and these results are also comparable to the 2009–2010 pandemic as our study reported a low incidence of sore throat (18.4%). In contrast to our study Approximately 54% of individuals presented with a painful throat, according to Chudasama et al. and Mehta et al.[21], [22]
Chawla et al showed most common presenting symptom fever present in 97.4% (n = 75) patients followed by cough (87%, n = 67) and Dyspnoea was present in 76% patients (n = 59). Only 32.5% patients (n = 25) had sore throat, while hemoptysis at presentation was present in only 9.1% cases (n = 7). Body ache was present in 15.6% (n = 12) cases, chest pain of non-cardiac cause in 5.2% (n = 4) cases, and altered sensorium in 2.6% (n = 2) cases.[18]
While in study of irio et al the typical influenza like illness with fever and cough, occasionally accompanied by other classical symp-toms (sore throat, myalgia, etc.) was present in most patients and some of them presented gastrointestinal symptoms.[17]
In another study by Tabrsi et.al the principal clinical symptoms leading to ICU admission were chest pain, hemoptysis, purulent sputum, altered mental status, loss of consciousness, and severe hypoxemia.[16]
Comorbities
In terms of related comorbidities, the most prevalent coexisting conditions were diabetes mellitus 12 (25%) followed by hypertension 10 (20.83%). Our results showed that 75 (79.7%) patients, had co-morbidities. Numerous earlier investigations have noted diabetes as a common comorbid illness. According to Kashinkunti et al., comorbidities of diabetes mellitus or hypertension occurred in approximately 45–50% of their cases.[2] Chudasama et al.also made note of the finding that bronchial asthma and COPD were the frequent risk factors in the US, however diabetes and hypertension were found to be widespread in India.[14] In a study conducted by Borse R T et al., 61% (n = 63) had concomitant conditions such as pregnancy (n = 13,20.63%), diabetes mellitus (DM) (n = 12,19.05%), HT (n = 11,17.60%), were major factors and obesity (n = 10, 15.87%), and rheumatic valve disease (RVHD) (n = 6,09.52%) minor factors. [19]
Radiological pattern
The bronco-vascular weft enhancement was the most common radiological pattern involved in influenza patients . When contrasting the findings with the various literature, Shi et al., Iorio et al. and Chawla et al discovered that infiltrates' presence was the predominant pattern. [23], [17], [18] Furthermore, we've seen studies that offer Findings that align with our findings, including those of. Vázquez-Agra et al. [14] Those patients who arrived in our research with radiological infiltrate died at a higher rate. In line with the results of the chest X-rays reported by Kashinkunti et al. and Puvanalingam et al., [4], [24] our investigation similarly revealed a greater frequency of lower zone involvement, with bilateral findings being more typical than unilateral. Bilateral lung infiltrates at initial presentation were linked to a higher rate of mechanical ventilation. The majority of patients had bilateral localisation on radiological evaluation while Right-sided localisation was more common than left-sided localisation. More patients exhibited lower zonal involvement. In sixteen cases, consolidation was observed. It was a typical discovery in our study . There were nodules and reticulonodular patterns seen. Borse, R. T. found ninety-one percent of patients had abnormal chest X-rays, whereas only nine percent had normal ones. In 61.53% of the cases, bilateral findings were seen. The most prevalent patterns were nodular (10.98%), reticulonodular (24.17%), and consolidation (64.83%).
Our findings concurred with those of investigations by Borse et al. [19] and Maheshwari M and Maheshwari S. [15] According to Maheshwari M and Maheshwari S [15] of 94 hospitalised patients with H1N1, sixty-eight (72%) showed bilateral opacities in the PA view of their chest X-ray. Among expired individuals, bilateral lower lobe infiltration [32 (34%)] was the most frequently observed X-ray chest finding.
Ventilation support
Of the patients, 57 (60.6%) required ventilatory assistance. The results of Borse et al., [19] who included 100 RT-PCR-confirmed cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection, were comparable to ours as 35 patients needed mechanical ventilation ,Four individuals required noninvasive mechanical ventilation (NIMV), whereas four patients who had previously been on NIMV needed to switch to IMV.. In a different investigation, Monika Maheshwari and Sanjeev Maheshwari from Rajasthan found that 57 (60.6%) of the patients needed ventilator assistance and total of 27 patients needed IMV (invasive mechanical ventilation). [15]
Additionally, it was discovered that early noninvasive ventilation-based respiratory support was beneficial in delaying the onset of respiratory failure and lowering the need for invasive ventilation in the majority of our patients. Although 16.9% of patients required an invasive ventilator, 40% of patients only needed non-invasive ventilator support.
Out of 48 cases, 42 patients were determined to have been discharged, and 6 cases died while receiving treatment. There was a 7:1 ratio between discharged and expired. Following containment of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, fewer cases have been reported worldwide. Unfortunately, since 2015, there has been a steady increase in H1N1-positive infections in India. While the survival rates have decreased from the pandemic period, there is still an increasing number of swab-positive individuals. The year of 2016 produced 1786 swab‐positive cases with 265 fatalities. Nonetheless, up until July 9, 2017, 12,460 swab-positive cases were identified in 2017. 600 of the patients in these circumstances passed away from the illness. The death rate appears to have decreased from 14.8% (2016) to 4% (2017), despite the fact that the data are unquestionably far higher than those from 2016.[25], [26]
Under the new recommendations of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, influenza A/H1N1 cases in India classified into three categories for management purposes. Cases falling under Category A don't require laboratory testing or antiviral therapy. Patients who fall under Category B include those with chronic illnesses, children, pregnant women, and those over 65. The treatment for these patients should consist of isoltamivir and isolation at home. Hospitalisation, laboratory tests, and oseltamivir therapy are required for patients classified as Category C.[4] Categorisation B or C comprised the majority of cases admitted to our hospital.
The influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 outbreak in India was reported in a recent paper by Murhekar and Mehendale, who concluded that the virus's pathogenicity is not significantly affected by any genetic changes. In[27] Our current study's results even indicate that the clinical profile seems to have stayed the same since the pandemic, but the death rate has unquestionably dropped, most likely as a result of early diagnosis and timely treatment commencement. It's possible to lower these figures even more. 28 people died in total, with 17 (or 60.71%) dying between the ages of 21 and 30. Patients in need of immediate therapy and a ventilator included those with TB and recurring chest infections. During five to seven days, we saw no appreciable adverse effects from the 150 mg twice day dose of oseltamivir. 51 patients (43.6%) recovered and were allowed to leave the hospital, while 53 patients (56.3%) passed away. Independent predictors of death included the onset of ARDS, involvement of both lower lung zones on a chest scan, need for a mechanical ventilator, and concomitant pregnancy (third trimester).
Mortality
With a total of 06 deaths in our study, the overall mortality rate was 12.5%; of them, 50% were in patients over 60.These outcomes corelate with other studies such as Lynfield et al. and Ramos et al., with death rates around 8%. [28], [29] Patients over 60 years had a greater death rate, in line with multiple prior earlier research, including Ramos et al. (over 80 years old), Huang et al., (individuals over 50) or Zhang et al..[27], [29], [30]
The patients included in our study were mostly referred cases and were more critically ill than the general population level, which would have contributed to increased mortality in the current Infectious Disease Division for management of swine flu H1N1 infection. [4] However, bilateral pneumonia on chest X-ray could be caused by cocomitent bacterial pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or progressive viral pneumonia. Overall, mortality in the present study was 12.5% (6/48), that was much higher than world wide mortality of 0.3-0.4%. [11], [12], [13], [14] Another Indian study also reported mortality of 5-7%. Approximately 6% case fatality rate was reported during the Rajasthani pandemic of 2015. [19] The Jaipur zone accounted for the highest number of cases (n=2801) and deaths (n= 101). The age group of 26 to 50 years old accounted for the greatest number of cases (2953/6203) and fatalities (52.11%; 197/378); females accounted for 52.64% of the deaths (199/378). Pregnancy was the main risk factor identified in 59.44 percent of the fatality cases, along with other associated risk factors. after the patients, 61.92 percent passed away within three days after being admitted to the hospital.
Respiratory distress syndrome and, in certain circumstances, multi-organ failure syndrome were the outcomes of other research, such as Rovina et al. [31] According to Arbat S. et al. [18] the case fatality ratio (CFR) was considerably greater in positive cases with a travel history, contact with swine flu cases, the need for invasive ventilator support, and involvement of more than three X-ray zones. Kshatriya R M et al. [20] recorded retrospective data on swine flu cases admitted at a tertiary care teaching hospital in 2015 and their result as either cured or expired. 40 people (61%) were men. Out of 65 patients, 55 (84.61%) had a cure (mean (SD) age of 50, while 10 patients (mean (SD) age of 51 passed away. The average age (SD) was 50.23 years, and the average (SD) number of hospital days was 6.32(3.3).
Conclusions
Epidemics serve as a continual reminder of the hidden risk even when the H1N1 pandemic has passed. Reducing the course of the disease and its accompanying mortality appears to be limited to vaccination, early diagnosis, and timely treatment . Due to the unpredictable nature of their clinical course, patients with risk factors need to get extra care. The death rate may be further reduced by careful diagnosis based on clinical signs and symptoms, biochemical and radiographic evaluation, and early therapy.
Recommendations
Reducing the number of illnesses can be achieved by routine immunisation against the most recent strains that are circulating. Given the high rate of pregnancy-related deaths, it is recommended that all expectant mothers receive the inactivated vaccine. Educating people about the disease's symptoms can facilitate early detection and treatment at medical facilities. Stable patients who do not require intensive care unit care should be advised to rest and practise appropriate coughing.
Limitations
Our results represent the experience of a single center in which the number of patients was too small for the proper evaluation of risk factors associated with mortality.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- SA Harper, K Fukuda, TM Uyeki, NJ Cox, CB Bridges. Prevention and control of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 2004. [Google Scholar]
- M Kashinkunti, S Gundikeri, M Dhananjaya. Study of clinical profile of patients with H1N1 influenza in a teaching hospital of North Karnataka. Diabetes 2013. [Google Scholar]
- LL Gaikwad, S Haralkar. Clinico-epidemiological profile of Influenza A H1N1 cases at a tertiary care institute of Uttarakhand. J Family Med Prim Care 2014. [Google Scholar]
- AC Cheng, T Kotsimbos, A Reynolds, SD Bowler, SG Brown, RJ Hancox. Clinical and epidemiological profile of patients with severe H1N1/09 pandemic influenza in Australia and New Zealand: an observational cohort study. BMJ Open 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- N Swine, FS Dawood, S Jain, L Finelli, MW Shaw, S Lindstrom. Virus Investigation Team. Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med 2009. [Google Scholar]
- M Khanna, P Kumar, K Choudhary, B Kumar, V Vijayan. Emerging influenza virus: a global threat. J Biosci 2008. [Google Scholar]
- R Perez-Padilla, D Rosa-Zamboni, SP Leon, M Hernandez, F Quiñones-Falconi, E Bautista. Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. N Engl J Med 2009. [Google Scholar]
- KK Patel, AK Patel, PM Mehta, RP Amin, KP Patel, PC Chuhan. Clinical outcome of novel H1N1 (Swine Flu)-infected patients during 2009 pandemic at tertiary referral hospital in western India. J Glob Infect Dis 2013. [Google Scholar]
- B Malhotra, R Singh, P Sharma, D Meena, J Gupta, A Atreya. Epidemiological & clinical profile of influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infections during 2015 epidemic in Rajasthan. Indian J Med Res 2016. [Google Scholar]
- T Samara, M Pawar, A Yadav. One Year of Experience with H1N1 Infection: Clinical Observations from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Northern India. Indian J Community Med 2011. [Google Scholar]
- W Cheng, Z Yu, S Liu, X Zhang, X Wang, J Cai. Comparison of influenza epidemiological and virological characteristics between outpatients and inpatients in Zhejiang Province. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- P Sharma, S Gupta, D Singh, S Verma, A Kanga. Kanga Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 cases in sub-Himalayan region. India Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2014. [Google Scholar]
- A Albarrán-Sánchez, C Ramírez-Rentería, F Huerta-Montiel, A Martínez-Jerónimo, A Herrera-Landero, JL García-Álvarez. Clinical features of patients with influenza-like illness who went to a third level center in the winter of. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc 2013. [Google Scholar]
- N Vázquez-Agra, V Alende-Castro, C Macía-Rodriguez, AT Marques-Afonso, M Vidal-Vazquez, VR Blanco. Prognostic Factors and Analytical Abnormalities in Patients Admitted With the Diagnosis of Influenza in a Third Level Hospital During the 2015–2016 Season. Open Respir Arch 2020. [Google Scholar]
- M Maheshwari, S Maheshwari. Clinico-Radiological Profile and Outcome of Novel H1N1-Infected Patients During 2009 to 2014 Pandemic at Tertiary Referral Hospital in Rajasthan. J Assoc Physicians India 2015. [Google Scholar]
- P Tabarsi, A Moradi, M Marjani, P Baghaei, SM Hashemian, SA Nadji. Factors associated with death or intensive care unit admission due to pan-demic 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection. Ann Thorac Med 2011. [Google Scholar]
- AM Iorio, B Camilloni, M Basileo, L Monaldi, E Lepri, M Neri. An Observational Retrospective Study Provide Information on Hospitalization and Severe Outcomes of the 2009 A(H1N1) Infection in Italy. J Clin Med Res 2013. [Google Scholar]
- R Chawla, S Kansal, M Chauhan, A Jain, BN Jibhkate. Predictors of mortality and length of stay in hospitalized cases of 2009 influenza A (H1N1): experiences of a tertiary care center. Indian J Crit Care Med 2013. [Google Scholar]
- R Borse, D Kadam, S Sangle, A Basavraj, H Prasad, P Umarji. Comparison of demographic, clinical, radiological characteristics and comorbidities in mechanically ventilated and nonventilated, adult patients admitted in ICU with confirmed diagnosis of influenza A (H1N1). J Assoc Physicians India 2013. [Google Scholar]
- S Arbat, M Dave, V Niranjane, I Rahman, A Arbat. Analyzing the clinical profile of swine flu/influenza A H1N1 infection in central India: a retrospective study. Virusdisease 2017. [Google Scholar]
- RK Chudasama, UV Patel, PB Verma, CD Amin, D Savaria, R Ninama. Clinico-epidemiological features of the hospitalized patients with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in Saurashtra region. Lung India 2009. [Google Scholar]
- AA Mehta, VA Kumar, SG Nair, F Joseph, G Kumar, SK Singh. Clinical profile of patients admitted with swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus infection: An experience from A tertiary care hospital. J Clin Diagn Res 2013. [Google Scholar]
- S J Shi, H Li, M Liu, Y M Liu, F Zhou, B Liu. Mortality prediction to hospitalized patients with influenza pneumonia: PO2/FiO2 combined lymphocyte count is the answer. Clin Respir J 2017. [Google Scholar]
- A Puvanalingam, C Rajendiran, K Sivasubramanian, S Ragunanthanan, S Suresh, S Gopalakrishnan. Case series study of the clinical profile of H1N1 swine flu influenza. J Assoc Physicians India 2011. [Google Scholar]
- B Cao, XW Li, Y Mao, J Wang, HZ Lu, YS Chen. Clinical features of the initial cases of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in China. N Engl J Med 2009. [Google Scholar]
- M Murhekar, S Mehendale. The 2015 influenza A (H1N1) pdm09 outbreak in India. Indian J Med Res 2016. [Google Scholar]
- JM Ramos, MM García-Navarro. Seasonal influenza in octogenarians and nona-genarians admitted to a general hospital: epidemiology, clinical presentation and prognostic factors. Rev Esp Quimioter 2016. [Google Scholar]
- R Lynfield, R Davey, D E Dwyer, M H Losso, D Wentworth, A Cozzi-Lepri. Outcomes of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection: results from two international cohort studies. PLoS One 2014. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- WT Huang, H Chang, YF Hsu, JH Chuang. Prognostic factors for mortality in patients hospitalized with influenza complications. Int Health 2015. [Google Scholar]
- G Weng, S Han, R Pu, WH Pan, L Shi. Risk factors for adult death due to 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus infection: a 2151 severe and critical cases analysis. Chin Med J 2013. [Google Scholar]
- N Rovina, M Erifaki, P Katsaounou, G Lyxi, A Koutsoukou, N G Koulouris. Subjects hospitalized with the 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) virus in a respiratory infection unit: clinical factors correlating with ICU admission. Respir Care 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Aims and Objectives
- Materials and Methods
- Results
- Demographic parameters
- Clinical parameters
- Distribution of co-morbidity
- Radiological findings
- Distribution of outcome
- Discussion
- Baseline characteristics
- Clinical features
- Comorbities
- Radiological pattern
- Ventilation support
- Mortality
- Conclusions
- Recommendations
- Limitations
- Source of Funding
- Conflict of Interest
