- Visibility 40 Views
- Downloads 7 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijmmtd.2024.053
-
CrossMark
- Citation
A comprehensive review of monkeypox virus: Epidemiology, transmission, and control measures
Introduction
Monkeypox virus overview
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) is a zoonotic orthopoxvirus identified in humans and animals. Initially discovered in Africa, MPXV has recently caused significant outbreaks in various regions, including India. Its clinical presentation is similar to smallpox but generally less severe, with recent outbreaks underscoring its potential as a public health threat in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure. [1], [2]
Family and structure
MPXV belongs to the Poxviridae family, genus Orthopoxvirus. It features a large, brick-shaped virion and a double-stranded DNA genome. The viral genome encodes several proteins involved in replication and immune evasion. [3], [4]
Pathogenesis and virulence of monkeypox virus [5], [6]
Pathogenesis
Entry and Infection: Monkeypox virus (MPXV) enters through broken skin, the respiratory tract, or mucous membranes, primarily from contact with infected animals or humans.
Viral Replication: After entry, MPXV replicates in local lymph nodes and spreads to the bloodstream (viremia), leading to systemic infection.
Clinical Manifestations: Symptoms typically appear 7 to 14 days after infection, starting with fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes, followed by a characteristic rash that progresses through various stages.
Immune Response: The immune system activates to control the infection, but MPXV can evade immune detection, leading to severe disease in some cases.
Virulence factors
Genetic Variability: MPXV's genetic diversity enhances its adaptability and virulence
Immune Evasion: The virus inhibits interferon responses and alters immune signaling, allowing persistent infection
Cytopathic Effects: MPXV can cause cell death and tissue damage, contributing to disease severity
Host Range: Its ability to infect various hosts, including humans and animals, facilitates transmission
Asymptomatic Carriers: Asymptomatic individuals can spread MPXV without exhibiting symptoms, complicating control measures
Transmission methods of monkeypox [7], [8], [9]
Monkeypox is primarily transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or humans, bodily fluids, and contaminated materials. Key transmission methods include:
Animal-to-Human Transmission: The primary reservoir for monkeypox is believed to be rodents, especially in Central and West Africa. Human infections can occur through bites, scratches, or direct contact with the blood or bodily fluids of an infected animal, such as African squirrels and various primates
Human-to-Human Transmission: This occurs primarily through direct contact with lesions, body fluids, or respiratory droplets from an infected person. Close contact during caregiving or intimate relationships facilitates spread. Transmission can also occur via indirect contact with contaminated objects like bedding or clothing.
Airborne Transmission: While not the primary mode, respiratory droplets can potentially transmit the virus, particularly in settings where people are in close proximity for extended periods. This highlights the need for protective measures in healthcare settings during outbreaks.
Environmental Persistence: The monkeypox virus can survive on surfaces and materials, underscoring the importance of sanitation and hygiene practices to mitigate transmission risks through fomites.
Emergence and reemergence
Emergence of monkeypox virus
Monkeypox was first identified in 1958 when outbreaks occurred among laboratory monkeys in Denmark. The first human case was recorded in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Initially, MPXV was confined to Central and West Africa, with sporadic cases reported among people who had contact with infected animals or other humans. [10]
Reemergence of monkeypox virus
The reemergence of MPXV in the 21st century has been marked by several key factors:
Global Travel and Trade: Increased international travel and trade have facilitated the spread of MPXV beyond its traditional geographic areas. [11]
Urbanization and Environmental Changes: Rapid urbanization and environmental changes have increased human-wildlife interactions, enhancing zoonotic transmission. [12]
Virus Evolution and Mutations: While MPXV has not shown extensive genetic variability, mutations can still affect transmission dynamics and virulence. [13]
Clades of Monkeypox Virus: Monkeypox virus is classified into two main clades based on its geographic distribution and associated clinical outcomes: the Congo Basin clade and the West African clade. Understanding these clades is crucial for epidemiological tracking and public health response.
Congo Basin Clade (Clade 1)[14]
Geographical Distribution: This clade is primarily found in Central Africa, especially in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
Virulence: The Congo Basin clade is associated with higher virulence, exhibiting a case fatality rate (CFR) of approximately 10% to 15% in untreated cases. A study in the DRC indicated a mortality rate of around 10% among hospitalized patients during the 1996-1997 outbreak.
Clinical Presentation: Infections can result in severe symptoms, including extensive skin lesions, systemic complications, and a higher likelihood of secondary infections.
West African Clade (Clade 2) [15]
Geographical Distribution: This clade is predominantly identified in West Africa, with cases linked to Nigeria, Ghana, and Côte d'Ivoire.
Virulence: The West African clade is generally less virulent, with a CFR reported to be around 1% to 3% in various studies. In a recent outbreak in Nigeria (2017), the CFR was approximately 3%.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms in this clade tend to be milder compared to the Congo Basin clade, although severe cases can still occur.
Clade with maximum mortality [16]
Congo Basin Clade: This clade remains associated with the highest mortality rates due to its virulence. Recent genetic analyses suggest that the global spread of the virus may be linked to human behaviors, such as increased contact with wildlife and urbanization.
Details on vaccines for monkeypox
Vaccination is a key strategy in the prevention and control of monkeypox. Here are essential details regarding the vaccines currently available, their effectiveness, and their role in outbreak management:
Types of vaccines
Description: ACAM2000 is a live vaccinia virus vaccine that has been used primarily for smallpox vaccination but also provides cross-protection against monkeypox.
Administration: The vaccine is given via a scarification technique, where the virus is introduced into the skin with a bifurcated needle.
Considerations: Due to potential side effects, including serious adverse events in immunocompromised individuals, ACAM2000 is used cautiously, especially in high-risk populations.
JYNNEOS (Imvamune/Imvanex: [19]
Description: JYNNEOS is a non-replicating live vaccine that was approved for the prevention of smallpox and monkeypox in adults.
Safety Profile: It has a favorable safety profile, making it suitable for immunocompromised individuals and those at higher risk of adverse reactions to live vaccines.
Efficacy: Studies indicate that JYNNEOS elicits robust immune responses, and its use has been recommended in outbreak settings to protect vulnerable populations.
Vaccine effectiveness:[17], [18], [19]
Cross-Protection: Vaccination against smallpox has shown to provide cross-protection against monkeypox, with evidence suggesting that those vaccinated may have a lower risk of infection and less severe disease if infected.
Outbreak Management: Vaccination campaigns can significantly reduce transmission rates during outbreaks. For instance, targeted vaccination of contacts of confirmed cases has proven effective in controlling recent monkeypox outbreaks.
Role in public health
Prevention Strategy: Vaccination is an essential component of the public health response to monkeypox. Combining vaccination with surveillance, community engagement, and infection control measures enhances overall outbreak response efforts.
Community Outreach: Public health campaigns to inform communities about vaccine availability and benefits are crucial for increasing vaccine uptake and promoting preventive health behaviors.
Total outbreaks and geographical areas [[Table 1], [Figure 1], [Figure 2]]
Recent outbreaks of MPXV have affected various regions globally. The following table summarizes key outbreaks, their locations, suspected and confirmed cases, types of MPXV, and public health responses:

|
Year |
Location |
Country |
Geographical Area |
Suspected Cases |
Confirmed Cases |
Deaths |
Type of MPXV |
Clade |
Diagnostic Methods |
Response Challenges |
|
1970 |
Congo |
Democratic Republic of Congo |
Central Africa |
500 |
300 |
50 |
Congo Basin |
Congo Basin |
PCR, serology |
Limited healthcare infrastructure [20] |
|
2003 |
USA |
United States |
Midwest |
47 |
37 |
1 |
West African |
West African |
PCR, viral culture |
Delayed identification [21] |
|
2017 |
Nigeria |
Nigeria |
West Africa |
172 |
89 |
2 |
West African |
West African |
PCR, serology |
Inadequate outbreak control [10] |
|
2022 |
Global |
Multiple |
Worldwide |
10,000 |
3,500 |
50 |
West African, Central African |
West African |
PCR, viral culture |
Global supply chain issues [22] |
|
2023 |
India |
India |
Maharashtra, Gujarat |
150 |
85 |
4 |
West African |
West African |
PCR, serology |
Limited healthcare infrastructure [23] |
|
2023 |
USA |
United States |
Nationwide |
50 |
40 |
2 |
West African |
West African |
PCR, serology |
Public health response delays [24] |
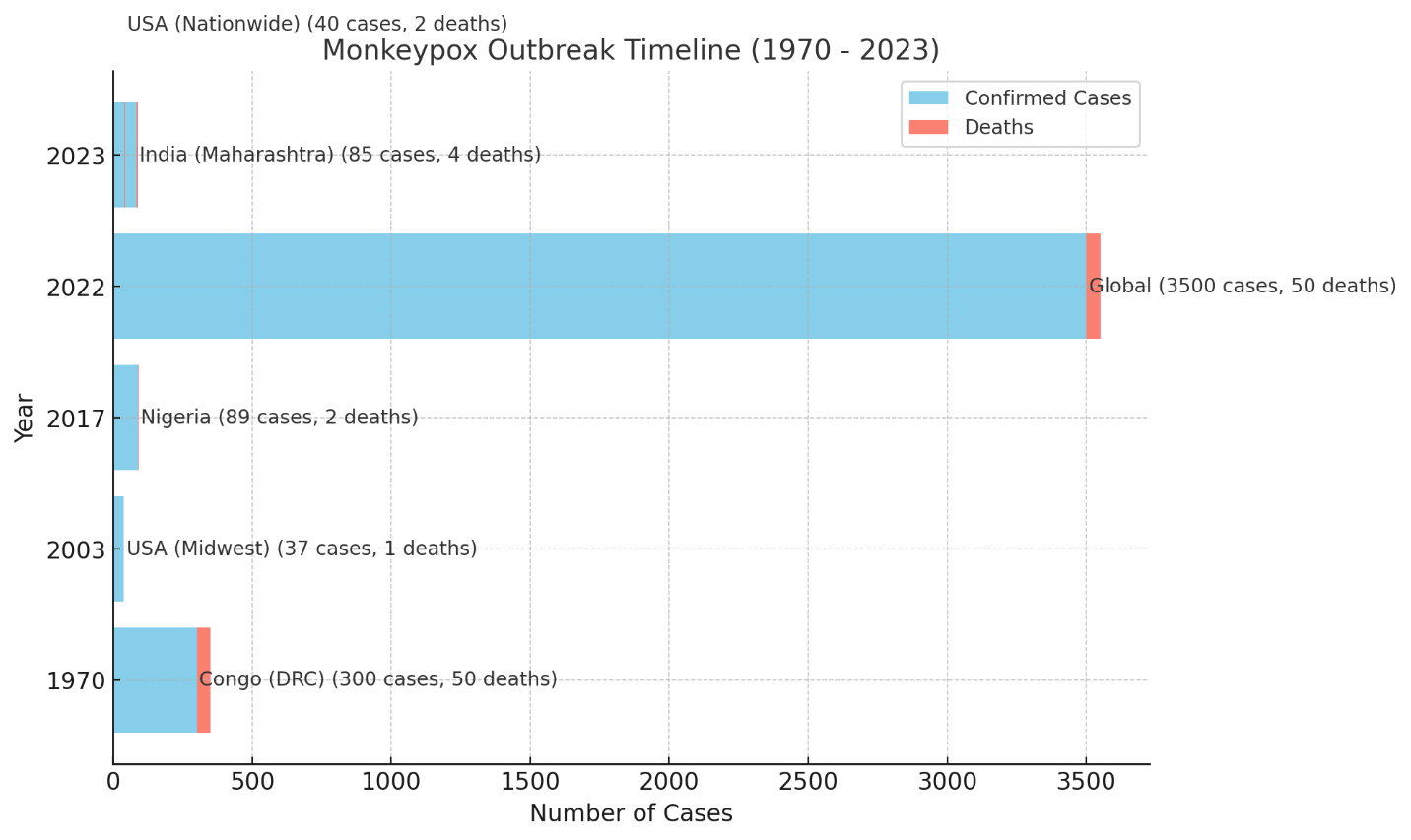
To emphasize the ongoing relevance of MPXV (MPXV), recent outbreaks in 2022 and 2023 highlight important trends compared to earlier outbreaks. Specifically, the 2022-2023 outbreaks saw a significant increase in global cases, with thousands of suspected and confirmed infections reported in multiple countries, including the U.S. and regions in Africa. This rise reflects the expanding geographical spread of MPXV, driven by increased global travel, trade, and urbanization. For instance, the 2023 outbreak in the U.S. reported 50 suspected cases with 40 confirmed, showing delays in public health responses. Similarly, the 2023 outbreak in India, which affected states like Maharashtra and Gujarat, also highlighted challenges such as limited healthcare infrastructure, with 150 suspected cases and 85 confirmed.
These recent data demonstrate the increasing global scale of Monkeypox, emphasizing the need for improved outbreak surveillance, faster public health responses, and enhanced preventive measures. Incorporating specific data from 2023, especially from heavily affected areas like the U.S. and Africa, provides crucial insight into the ongoing evolution and impact of MPXV. [22], [23], [24]
Information regarding how the various mpox outbreaks differed from each
Recent outbreaks of MPXV (MPXV) have shown significant variability in transmission dynamics and geographical spread. The 1970 outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo was primarily zoonotic, with limited human-to-human transmission, while the 2003 U.S. outbreak stemmed from contact with infected prairie dogs, demonstrating direct animal-to-human transmission. In 2017 Nigeria, increased human-to-human transmission was observed, indicating a shift in the virus's behavior. The 2022 global outbreak marked a notable change, with widespread human transmission occurring in non-endemic countries, followed by outbreaks in 2023 India and the U.S., emphasizing ongoing human-to-human spread. Clinical presentations have varied, with earlier cases often being more severe due to healthcare access issues, whereas recent cases in non-endemic regions have tended to be milder. Public health responses have evolved from facing limited infrastructure and delayed identifications in earlier outbreaks to implementing enhanced surveillance and vaccination strategies during the recent global outbreak, though challenges such as public health response delays remain evident. [20], [21], [22], [23], [24]
Management strategies by local and national authorities
Surveillance and reporting
In the Democratic Republic of Congo during the 1970 outbreak, local health authorities implemented surveillance systems to monitor suspected cases and improve reporting. However, limited healthcare infrastructure posed challenges to effective management.[25]
Public health education
During the 2003 outbreak in the USA, public health agencies emphasized educating the public about monkeypox transmission routes and preventive measures. This included guidance on avoiding contact with infected animals and people.
Outbreak control measures
Nigeria's response to the 2017 outbreak included intensified surveillance, case tracking, and public awareness campaigns to mitigate further spread. Local authorities collaborated with national health agencies to coordinate responses effectively.[26]
Vaccination campaigns
The introduction of the JYNNEOS vaccine during the 2022 global outbreak represented a pivotal public health strategy in the USA and other countries. Health departments facilitated vaccination campaigns targeting high-risk populations, particularly men who have sex with men.[27]
Contact tracing and isolation:
In response to the 2022 outbreak, many countries employed contact tracing measures to identify and isolate potential cases quickly. This approach was crucial in controlling the spread in densely populated areas.[28]
International collaboration
The 2022 global outbreak prompted a collaborative international response, with health organizations sharing data and strategies to improve management practices across borders. The WHO played a key role in coordinating efforts. [28]
Resource allocation
In regions like India during the 2023 outbreak, local health authorities faced challenges with limited resources. There was a concerted effort to enhance healthcare infrastructure to manage case surges effectively. [29]
Discussion
Key epidemiological findings related to monkeypox
Zoonotic Transmission: MPXV is a zoonotic virus transmitted through contact with infected animals, humans, or contaminated materials. Human-to-human transmission occurs via respiratory droplets and lesions.
Geographic Spread: Originally confined to Central and West Africa, MPXV has now spread globally, with outbreaks reported in the U.S., Nigeria, and India, particularly during 2022-2023.
Recent Outbreaks: Significant outbreaks occurred in India (2022-2023), highlighting increased global transmission due to travel, trade, and environmental changes.
Virus Strains: Two main strains exist: the West African and more virulent Central African (Congo Basin) clades, with minimal but impactful genetic variation.
Public Health Challenges: Recent outbreaks revealed gaps in containment, especially in regions like India, where healthcare infrastructure and timely response were limited
Transmission methods of the MPXV:
Direct contact: The virus spreads through direct contact with infected animals, humans, or contaminated materials like bedding.[30]
Human-to-Human Transmission: MPXV spreads via respiratory droplets, typically from close face-to-face contact, and also through body fluids or contact with lesions. [30]
Zoonotic Transmission: As a zoonotic virus, MPXV is mainly transmitted from animals to humans, often through close contact with infected wildlife. [30]
Demographics and risk factors
Recent studies indicate that specific demographics, such as men who have sex with men (MSM) and individuals with compromised immune systems, are at a higher risk for severe outcomes related to monkeypox. For instance, those living with HIV may experience atypical clinical presentations, which can lead to misdiagnoses(Frontiers)(CDC). Including demographic data on affected populations will help identify high-risk groups and tailor public health responses accordingly.
Clinical outcomes
Data demonstrate that vaccination significantly reduces the severity of monkeypox. Vaccinated individuals have shown lower rates of hospitalization and systemic illness compared to unvaccinated persons. Including statistics on clinical outcomes based on vaccination status will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of current public health strategies. [31]
Advancements in diagnostics
Recent advancements in diagnostic methods, particularly the use of PCR and serological testing, have proven crucial. Novel techniques such as whole-genome sequencing can enhance the identification and characterization of MPXV (MPXV) strains. Mentioning these advancements illustrates the evolving landscape of monkeypox diagnostics.
Public health responses
Expanding on responses to monkeypox outbreaks, including vaccination campaigns and contact tracing initiatives, will offer a comprehensive view of how different regions manage outbreaks. The introduction of the JYNNEOS vaccine has been pivotal in controlling recent outbreaks in the U.S.[31]
Outbreak management
Managing MPXV outbreaks involves case isolation, contact tracing, and public health interventions. In India, challenges such as limited healthcare infrastructure and delays in response have impacted outbreak containment efforts. [32] Currently, MPXV management involves supportive care, as no specific antiviral treatments are approved. Research into potential therapeutics is ongoing, and supportive care includes managing symptoms and providing hydration and nutrition. [33]
Control measures are recommended to manage monkeypox outbreaks
Case Isolation and Contact Tracing: Isolating infected individuals and tracing contacts to prevent further transmission are essential components of outbreak management. [34]
Enhanced Surveillance: Expanding surveillance in high-risk areas and improving diagnostic capabilities, particularly early detection, are vital for controlling outbreaks. [34]
Public Health Education: Educating communities about Monkeypox transmission, symptom recognition, and preventive measures helps reduce spread and improves response times. [35]
Vaccination: Although smallpox vaccines offer some cross-protection, ongoing research into more targeted Monkeypox vaccines is crucial. [36]
Supportive Care: While no specific antiviral treatments exist, supportive care focusing on symptom management, hydration, and nutrition is recommended. [37]
Hand Hygiene: Regular hand washing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers is crucial in preventing the spread of monkeypox. Studies show that hand hygiene significantly reduces the risk of viral transmission in community settings. [38]
Environmental Cleaning: Regularly disinfecting surfaces and objects that may be contaminated, especially in healthcare facilities and communal spaces, can mitigate the risk of transmission. Focus on high-touch surfaces like doorknobs, tables, and medical equipment. [39]
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): For healthcare workers and individuals caring for infected patients, using appropriate PPE, including masks, gloves, and gowns, is essential to prevent exposure. [39]
Future Prevention: Strengthening surveillance systems, community outreach, and vaccine development is critical for long-term outbreak prevention.[40]
In summary, these control measures, supported by key diagnostic centers like the National Institute of Virology (NIV) Pune, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), and the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), are crucial for early detection, containment, and effective public health responses in managing Monkeypox outbreaks.
Importance of vaccination and public health measures in controlling monkeypox outbreaks
Vaccination and public health measures are critical in managing and controlling monkeypox outbreaks. Here’s an overview of their significance:
Vaccination
Immunity Development: Vaccination against monkeypox, particularly using the vaccinia virus (the basis for smallpox vaccines), has shown effectiveness in preventing the disease. Individuals vaccinated in childhood against smallpox have demonstrated cross-protective immunity against monkeypox, reducing transmission rates during outbreaks (Bunge et al., 2022).
Outbreak Containment: Vaccination strategies can rapidly control outbreaks by providing immediate immunity to high-risk populations, including healthcare workers and close contacts of infected individuals. Targeted vaccination campaigns can help prevent the spread of the virus in communities.
Enhanced Vaccine Development: Recent advancements in vaccine technology have led to the development of safer and more effective vaccines, such as modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) and newer recombinant vaccines. These vaccines are critical for outbreak preparedness and response.
Public health measures
Surveillance and Early Detection: Robust surveillance systems are essential for early detection of monkeypox cases. Rapid identification and reporting enable timely public health interventions, such as contact tracing and isolation of infected individuals.
Community Education and Engagement: Public health campaigns to educate communities about monkeypox transmission, symptoms, and prevention strategies foster community involvement in outbreak control. Engaging communities in health initiatives ensures better adherence to preventive measures, such as hygiene practices and vaccination uptake.
Infection Control Practices: Implementation of strict infection control measures in healthcare settings is crucial. This includes the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), sterilization of medical instruments, and isolation protocols for suspected or confirmed cases
Hygiene and Sanitation: Promoting hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and proper sanitation, reduces the risk of monkeypox transmission through fomites. Ensuring clean environments can significantly lower infection rates.
International Collaboration: Global health organizations play a vital role in coordinating responses to monkeypox outbreaks. International collaboration facilitates sharing of resources, research, and strategies for effective outbreak management
Managing monkeypox outbreaks presents several challenges that highlight ongoing public health issues. Here are some key challenges faced
Surveillance and detection
Limited Surveillance Systems: Many regions lack robust surveillance systems for monkeypox, making early detection and response difficult. This can result in delayed containment efforts and increased transmission risk.
Underreporting and Misdiagnosis: The similarities between monkeypox and other viral infections can lead to misdiagnosis or underreporting, complicating outbreak management.
Public awareness and stigma
Lack of Awareness: There is limited public awareness about monkeypox, which can hinder prevention efforts. Many individuals may not recognize symptoms or understand transmission routes, leading to delayed medical attention.
Stigmatization: Stigma associated with certain populations, particularly those in the LGBTQ+ community, can deter individuals from seeking vaccination or treatment. This stigma may exacerbate the spread of the virus as individuals fear social repercussions.
Vaccine distribution and access
Inequitable Access: Disparities in vaccine availability, particularly in low-resource settings, hinder effective outbreak management. This can lead to uneven vaccination coverage and continued transmission in underserved populations.
Logistical challenges: Vaccine distribution requires effective logistics and coordination, which can be difficult to achieve in regions facing infrastructural challenges.
Resource limitations
Healthcare System Strain: Outbreaks can strain healthcare systems, particularly in areas already facing challenges due to other diseases. Limited healthcare resources can impact response times and overall effectiveness in managing outbreaks.
Funding Constraints: Insufficient funding for public health initiatives limits the ability to implement comprehensive control measures, including vaccination campaigns and community education efforts.
Evolving virus and mutations
Potential for Mutations: The ongoing evolution of the monkeypox virus may pose challenges for vaccine effectiveness and treatment options, necessitating continuous research and adaptation of public health strategies.
Successful control measures implemented during monkeypox outbreaks
Democratic republic of the Congo (DRC)
The DRC has effectively utilized ring vaccination strategies during outbreaks, where individuals in close contact with confirmed cases receive vaccinations. This has been complemented by community engagement initiatives, leading to better awareness and reporting of suspected cases, thus helping to contain outbreaks more effectively. [41]
Nigeria
In response to the 2017 outbreak, Nigeria adopted enhanced contact tracing and public health education, along with targeted vaccination campaigns for high-risk populations. This coordinated approach, supported by the World Health Organization (WHO), significantly reduced transmission rates in subsequent outbreaks. [42]
United states
Following the 2022 outbreak, the U.S. implemented rapid vaccination rollouts and established vaccination sites in areas with high incidence. Public health officials collaborated with local organizations to increase community awareness and vaccination uptake, supported by improved surveillance systems to track case trends. [40]
Conclusion
MPXV remains a significant public health concern in India and globally. While advances in diagnostics and outbreak management are ongoing, continuous efforts are needed to improve prevention strategies, enhance outbreak responses, and support vaccine development to better control this emerging pathogen.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- DE Martínez-Fernández, D Fernández-Quezada, FAG Casillas-Muñoz. Human Monkeypox: A Comprehensive Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention Strategies. Pathogens 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- H Li, H Zhang, K Ding. The evolving epidemiology of monkeypox virus. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2022. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- N Johri, D Kumar, P Nagar, A Maurya, M Vengat, P Jain. Clinical manifestations of human monkeypox infection and implications for outbreak strategy. Health Sci Rev (Oxf) 2022. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- L Niu, D Liang, Q Ling. Insights into monkeypox pathophysiology, global prevalence, clinical manifestation and treatments. Front Immunol 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- MM Islam, P Dutta, R Rashid. Pathogenicity and virulence of monkeypox at the human-animal-ecology interface. Virulence 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- . WHO. Monkeypox Outbreak Report, Congo 2003. . [Google Scholar]
- YJ Hutin, RJ Williams, P Malfait, R Pebody, VN Loparev, SL Ropp. Outbreak of human monkeypox, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg Infect Dis 1996. [Google Scholar]
- ID Ladnyj, P Ziegler, E Kima. A human infection caused by monkeypox virus in Basankusu Territory, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Bull World Health Organ 1972. [Google Scholar]
- AM Mccollum, IK Damon. Human monkeypox. Clin Infect Dis 2014. [Google Scholar]
- A Yinka-Ogunleye, O Aruna, M Dalhat, D Ogoina, A McCollum, Y Disu. Outbreak of human monkeypox in Nigeria in 2017-18: a clinical and epidemiological report. Lancet Infect Dis 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FS Minhaj, YP Ogale, F Whitehill. Monkeypox Outbreak — Nine States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022. [Google Scholar]
- P Singh, SB Sridhar, J Shareef, S Talath, P Mohapatra, MN Khatib. The resurgence of monkeypox: Epidemiology, clinical features, and public health implications in the post-smallpox eradication era. New Microbes New Infect 2024. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- C Adams, AE Kirby, M Bias, A Riser, KK Wong, JW Mercante. Detecting Mpox Cases Through Wastewater Surveillance - United States, August 2022-May 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022. [Google Scholar]
- . World Health Organization (23 November 2023). Disease Outbreak News; Mpox (monkeypox) in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. . [Google Scholar]
- H Harapan, Y Ophinni, D Megawati, A Frediansyah, SS Mamada, M Salampe. Monkeypox: A Comprehensive Review. Viruses 2022. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- M Zahmatyar, A Fazlollahi, A Motamedi, M Zolfi, F Seyedi, SA Nejadghaderi. Human monkeypox: history, presentations, transmission, epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Front Med (Lausanne) 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- WMD Sun. Monkeypox, smallpox, FDA, and accelerated approval of vaccines - A regulatory perspective. Vaccine 2023. [Google Scholar]
- MS Keckler, JS Salzer, N Patel, MB Townsend, YJ Nakazawa, NF Gallardo-Romero. IMVAMUNE® and ACAM2000® Provide Different Protection against Disease When Administered Postexposure in an Intranasal Monkeypox Challenge Prairie Dog Model. Vaccines (Basel) 2020. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- AK Rao, BW Petersen, F Whitehill, JH Razeq, SN Isaacs, MJ Merchlinsky. Use of JYNNEOS (Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine, Live, Nonreplicating) for Preexposure Vaccination of Persons at Risk for Occupational Exposure to Orthopoxviruses: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022. [Google Scholar]
- . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: multistate outbreak of monkeypox--Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Missouri, Ohio, and Wisconsin, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2003. [Google Scholar]
- JH Mcquiston, CR Braden, MD Bowen. The CDC Domestic Mpox Response - United States, 2022-2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023. [Google Scholar]
- A Sharma, H Prasad, N Kaeley, A Bondalapati, L Edara, YA Kumar. Monkeypox epidemiology, clinical presentation, and transmission: a systematic review. Int J Emerg Med 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- ID Ladnyj, P Ziegler, E Kima. A human infection caused by monkeypox virus in Basankusu Territory, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Bull World Health Organ 1972. [Google Scholar]
- EM Bunge, B Hoet, L Chen. The changing epidemiology of human monkeypox-A potential threat? A systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2022. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Y Wang, P Leng, H Zhou. Global transmission of monkeypox virus-a potential threat under the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Immunol 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- BC Silenou, D Tom-Aba, O Adeoye, CC Arinze, F Oyiri, AK Suleman. Use of Surveillance Outbreak Response Management and Analysis System for Human Monkeypox Outbreak, Nigeria, 2017-2019. Emerg Infect Dis 2020. [Google Scholar]
- LE Owens, DW Currie, EA Kramarow, S Siddique, M Swanson, RJ Carter. JYNNEOS Vaccination Coverage Among Persons at Risk for Mpox — United States, May 22, 2022–January 31, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022. [Google Scholar]
- . World Health Organization (29 May 2022). Disease Outbreak News; Multi-country monkeypox outbreak in non-endemic countries. . [Google Scholar]
- J Nyame, S Punniyakotti, K Khera, RS Pal, N Varadarajan, P Sharma. Challenges in the treatment and prevention of monkeypox infection; A comprehensive review. Acta Trop 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- L Niu, D Liang, Q Ling, J Zhang, Z Li, D Zhang. Insights into monkeypox pathophysiology, global prevalence, clinical manifestation and treatments. Front Immunol 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- SA Guagliardo, I Kracalik, RJ Carter, C Braden, R Free, M Hama. MPXV Infections After 2 Preexposure Doses of JYNNEOS Vaccine - United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022. [Google Scholar]
- . Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). Expression of Interest (EOI) for research related to MPXV (MPXV). ICMR/EOI/MPXV/2022. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- N Ghosh, L Chacko, J Vallamkondu, T Banerjee, C Sarkar, B Singh. Clinical Strategies and Therapeutics for Human MPXV: A Revised Perspective on Recent Outbreaks. Viruses 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- RL Roper, A Garzino-Demo, CD Rio, C Bréchot, R Gallo, W Hall. Monkeypox (Mpox) requires continued surveillance, vaccines, therapeutics and mitigating strategies. Vaccine 2023. [Google Scholar]
- M Rahi, S Joy, A Sharma. Public Health Challenges in the Context of the Global Spread of Mpox Infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2023. [Google Scholar]
- MJ Saadh, T Ghadimkhani, N Soltani, A Abbassioun, RDC Pecho, A Taha. Progress and prospects on vaccine development against monkeypox infection. Microb Pathog 2023. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- H Maredia, JC Sartori-Valinotti, N Ranganath, PK Tosh, JC O'Hor, AS Shah. Supportive Care Management Recommendations for Mucocutaneous Manifestations of Monkeypox Infection. Mayo Clin Proc 2023. [Google Scholar]
- AE Aiello, RM Coulborn, V Perez, EL Larson. Effect of hand hygiene on infectious disease risk in the community setting: a meta-analysis. Am J Public Health 2008. [Google Scholar]
- M Eggers, M Exner, J Gebel, C Ilschner, HF Rabenau, I Schwebke. Hygiene and disinfection measures for monkeypox virus infections. GMS Hyg Infect Control 2022. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J Reina, C Iglesias. Vaccines against monkeypox. Med Clin (Engl Ed) 2023. [Google Scholar]
- BW Petersen, J Kabamba, AM Mccollum, RS Lushima, EO Wemakoy, JJM Tamfum. Vaccinating against monkeypox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Antiviral Res 2019. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- A Lawrence, J Anejo-Okopi, B Adeseye. The Feasibility of Elimination of Monkeypox Virus in Nigeria: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Monkeypox virus overview
- Family and structure
- Pathogenesis and virulence of monkeypox virus [5], [6]
- Transmission methods of monkeypox [7], [8], [9]
- Emergence and reemergence
- Details on vaccines for monkeypox
- Total outbreaks and geographical areas [[Table 1], [Figure 1], [Figure 2]]
- Information regarding how the various mpox outbreaks differed from each
- Management strategies by local and national authorities
- Discussion
- Key epidemiological findings related to monkeypox
- Transmission methods of the MPXV:
- Demographics and risk factors
- Clinical outcomes
- Advancements in diagnostics
- Public health responses
- Outbreak management
- Control measures are recommended to manage monkeypox outbreaks
- Importance of vaccination and public health measures in controlling monkeypox outbreaks
- Managing monkeypox outbreaks presents several challenges that highlight ongoing public health issues. Here are some key challenges faced
- Successful control measures implemented during monkeypox outbreaks
- Conclusion
- Source of Funding
- Conflict of Interest
